Risk management and compliance are essential guardrails for AI projects, helping avoid fines, protect brand reputation, and maintain operational continuity. They serve as the road map and traffic rules guiding enterprise AI systems.
Navigating Risk Management And Compliance For Enterprise AI

Enterprise AI initiatives are complex and, without clear standards, teams risk regulatory violations or operational delays. This guide provides the strategic framework required for effective risk management and compliance.
In 2025, the Governance, Risk Management and Compliance (GRC) market in Germany was estimated at approximately USD 50.2 billion, with a projected CAGR of 15.1 % through 2033, driven by enterprise investment in compliance automation and risk analytics. Discover more about the GRC market growth in Germany in the full research report.
- Reduces fines and reputational risk through consistent policies and automated checks
- Speeds up innovation by integrating governance and risk assessments in advance
- Builds stakeholder confidence with transparent controls and audit trails
Organizations embedding compliance automation early report up to a 40 % reduction in incident response time. Aligning with GDPR fundamentals at the outset can also halve audit costs.
Building A Trust Foundation
Defining governance roles and structures provides the necessary oversight for AI initiatives. Assign responsibilities—such as Chief Risk Officer or Data Protection Officer—early to ensure clear accountability.
“Structured processes and controls form the foundation of trust in AI deployment.”
This roadmap covers:
- Core definitions and an AI risk taxonomy
- Leading frameworks: ISO 31000, TISAX and GDPR
- Governance models, role assignments and implementation steps
Subsequent sections provide practical tips, checklists, KPIs and industry examples from automotive, manufacturing and finance.
Explaining Risk Management And Compliance Frameworks
Most organizations treat ISO 31000, TISAX and GDPR as compliance checkboxes rather than operational toolkits. In practice, each offers a distinct playbook:
Frameworks As Toolkits
- ISO 31000 defines risk terminology and a process-driven structure adaptable to any context.
- TISAX establishes security requirements for automotive OEMs and tier suppliers.
- GDPR codifies individual privacy rights and mandates robust data-handling practices.
This diagram highlights the five core principles of ISO 31000, guiding risk identification, evaluation, reporting and continuous improvement.
Comparison Of Risk Management And Compliance Frameworks
| Framework | Focus Area | Applicability |
|---|---|---|
| ISO 31000 | Holistic risk management blueprint | Cross-industry, including AI initiatives |
| TISAX | Information security in automotive | OEMs and tier suppliers |
| GDPR | Personal data privacy and protections | Any EU-based or EU-processing entity |
Combining multiple frameworks covers blind spots and streamlines audits by reducing overlap.
Germany has tightened statutory requirements since 2021, expanding supply-chain due diligence under the German Supply Chain Due Diligence Act and non-financial reporting via the EU CSRD. These shifts drive new IT control investments and staffing. Learn more about regulatory updates driving IT control investments and staffing at MetricStream.
Mapping each framework clause to a governance role—like Chief Risk Officer or Data Protection Officer—ensures clear ownership of risk assessments, control deployment and compliance reporting.
If you want deeper insights into building audit-proof AI systems, check out our guide on audit-proof AI systems
Ready to Build Your AI Project?
Let's discuss how we can help you ship your AI project in weeks instead of months.
Combining general risk frameworks and targeted compliance standards delivers robust, scalable governance for enterprise AI.
Choosing The Right Mix
Select frameworks that match your sector and data sensitivity:
- Assess Your Scope
- Map Requirements
- Define Roles
- Review Overlaps
- Measure Progress
Practical Integration Tips
- Automate GDPR privacy checks with rule-based scans
- Schedule quarterly audits across ISO 31000 processes and TISAX controls
- Build dashboards showing risk trends, control statuses and audit results
- Provide targeted training on specific clauses and their operational impact
Quick Reference Checklist
- Define risk categories aligned to ISO 31000 principles
- Embed TISAX requirements into supplier and vendor assessments
- Apply GDPR’s privacy-by-design ethos across data pipelines
- Document roles, responsibilities and reporting lines in a governance charter
- Update controls after model releases or regulation changes
Key Components Of AI Risk Management And Compliance
AI risk management and compliance are central to trustworthy AI deployment. Continuous monitoring detects drift or performance dips before they escalate. Each module below links to policies, automated controls and governance roles.
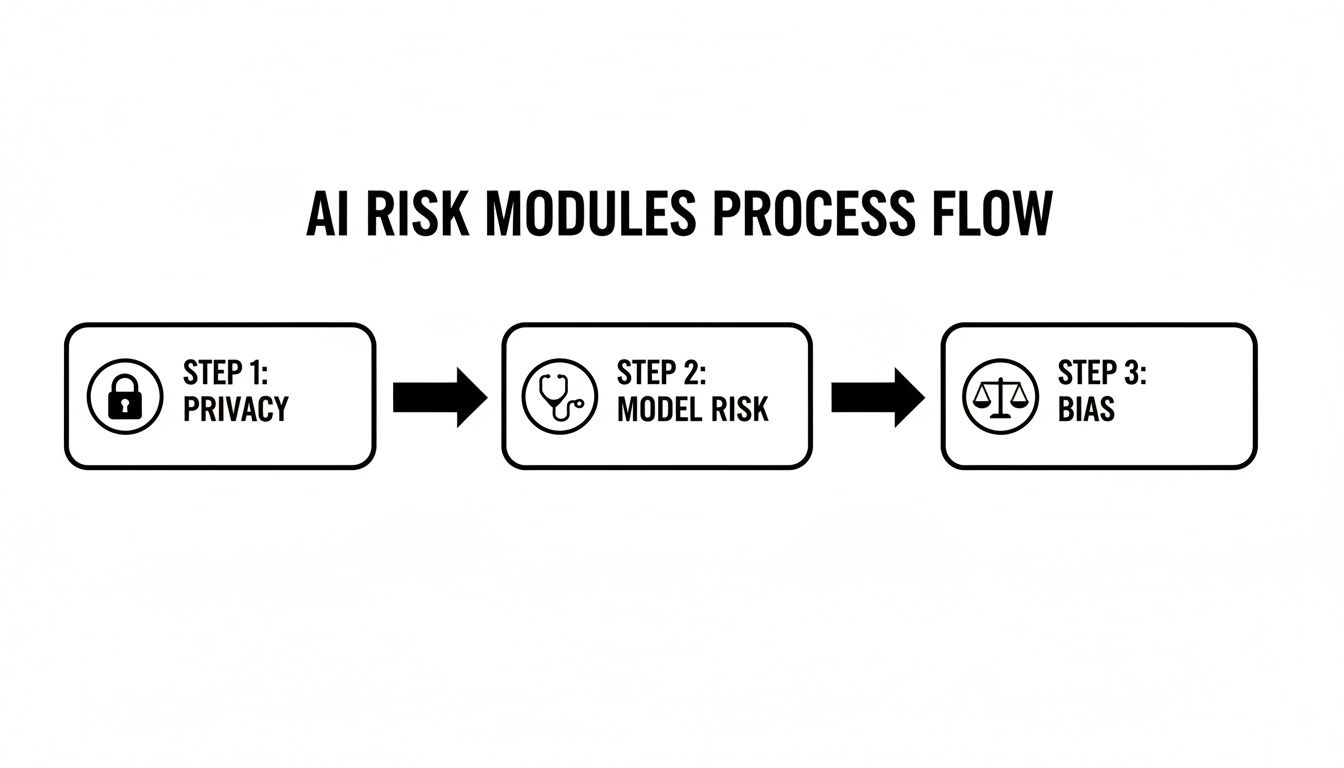
Data Privacy And Protection
Key Controls:
- Encryption at Rest and in Transit
- Role-Based Access
- Data Anonymisation and Pseudonymisation
- Automated Lineage Logs
These align with GDPR and local privacy rules, ensuring data integrity and audit readiness.
Model Risk And Bias
Mitigation Steps:
- Validate incoming data accuracy
- Calculate fairness metrics (e.g., demographic parity)
- Use explainable AI tools for decision transparency
- Set drift thresholds to trigger retraining
Continuous oversight turns a black box into a reliable partner.
Cybersecurity And Governance
Focus Areas:
- Infrastructure hardening and vulnerability scans
- Intrusion detection with real-time alerts
- Automated security tests in CI/CD pipelines
- Defined escalation paths through governance bodies
Role Definitions And Responsibilities
| Role | Responsibility |
|---|---|
| Chief Risk Officer | Owns enterprise risk strategy and oversight |
| AI Ethics Committee | Evaluates ethical impacts and approves design principles |
| Data Protection Officer | Enforces GDPR compliance and manages privacy initiatives |
Executive surveys report 85 % of respondents see rising compliance complexity, with 49 % automating eleven or more compliance tasks. Focus areas include training (82 %), risk assessments (76 %) and continuous monitoring (75 %). Read the full global compliance complexity survey.
Check our AI security and compliance services in Germany at Reruption GmbH.
Controls And Continuous Monitoring
- Performance Metrics & Drift Thresholds
- Security Incident Dashboards
- Compliance Audit Logs
- Training Completion Trackers
Integration Into Daily Operations
A living control framework keeps AI safe by design.
Regular retrospectives and internal audits refine processes, embedding best practices over time.
Practical Example
In an automotive scenario:
- Data ingestion secured under TISAX guidelines
- Model validation checkpoints as quality gates
- Network segmentation limiting lateral movement
This approach cut audit findings by 30 % within six months.
Roadmap To Implement Risk Management And Compliance
Implementing risk management and compliance in AI requires clear milestones and checkpoints to ensure progress and regulatory alignment. This roadmap guides managers and C-level leaders through each stage.
Assessment And Benchmarking
Conduct interviews, review documentation and run surveys to uncover gaps in data privacy, model bias and operational risk. Translate findings into a heatmap highlighting priority risk areas.
Designing Controls And Policies
Draft policies covering data ingestion, model testing and incident escalation:
- Access Controls: Multi-factor authentication
- Validation Checks: Output thresholds triggering reviews
- Monitoring Dashboards: Real-time tracking of drift, security logs and audit trails
Tie each policy to an approval workflow.
Selecting Technology Tools
Evaluate platforms on:
- Data lineage capabilities
- Policy enforcement engines
- Audit-logging and alerting features
Ensure encryption, role-based permissions and real-time notifications.
Want to Accelerate Your Innovation?
Our team of experts can help you turn ideas into production-ready solutions.
Piloting And Scaling
- Define scope and success indicators
- Simulate data flows and test detection logic
- Log issues, apply fixes and verify control effectiveness
Training And Communication
Run workshops and scenario drills. Update materials to reflect emerging risks and regulations.
“Consistent training turns compliance from a task into a habit.”
Continuous Monitoring And Audits
- Quarterly Audits
- Monthly Performance Reviews
- Annual Policy Refreshes
Document findings, apply remediations and report progress to the governance board.
Scaling And Evolution
Embed controls across the organization. Integrate risk tasks into roadmaps and sprint plans. For a structured rollout, see 21-Day AI Delivery Framework.
Key Tips And Pitfalls
- Prioritise high-impact controls within 30 days
- Assign clear owners and set realistic deadlines
- Schedule mid-pilot check-ins
- Celebrate small victories
Maintaining Momentum
Hold regular retrospectives and track metric trends. Share lessons to maintain stakeholder engagement.
“Ongoing refinement separates successful risk programmes from static checklists.”
Next Steps
- Schedule a risk assessment workshop within two weeks
- Appoint a cross-functional steering committee led by the Chief Risk Officer
- Develop a heatmap of AI risk modules and control gaps
- Select a pilot use case and define success criteria
Measuring Success With KPIs And Metrics
If you can’t measure it, you can’t improve it. A balanced mix of quantitative and qualitative KPIs gives a complete view—from incident counts to cultural readiness.
Defining Your Core Metrics
- AI Risk Events Logged
- Mean Time to Incident Resolution
- Audit Finding Trends
- Training Completion Rate
SMART criteria turn abstract goals into actionable measures that drive governance decisions.
Risk Management KPI Metrics
| Metric | Description | Target | Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|
| AI Risk Events | Count of new risk incidents identified | < 5 per month | Monthly |
| Incident Resolution Time | Average hours from report to closure | < 48 hours | Weekly |
| Audit Findings Trend | Net change in findings versus previous period | ≥ 10 % reduction | Quarterly |
| Training Completion Rate | Percentage of staff completing mandatory modules | 100 % | Monthly |
Building Executive Dashboards
- Select metrics aligned with risk appetite and regulations
- Use color-coded alerts for breaches or anomalies
- Arrange charts to highlight trends and targets
- Automate data feeds to eliminate manual updates
- Schedule governance meetings using dashboard exports
A German manufacturing division cut mean resolution time by 35 % in two quarters by fine-tuning alerts and routing.
Best Practices For KPI Programmes
- Pilot a dashboard with three high-impact metrics
- Use rolling averages to smooth out spikes
- Add explanatory captions for unusual trends
- Archive historical data to illustrate progress
Dive deeper into advanced analytics in intelligent monitoring by Reruption GmbH.
Industry Examples In Automotive Manufacturing And Finance

Automotive Case With TISAX Audit
A tier-1 automotive supplier mapped TISAX controls to AI data pipelines in six weeks. By maintaining a living risk register and prioritising encryption, access reviews and supplier questionnaires, non-conformance issues fell by 50 % in the first audit cycle.
Automotive Implementation Tips
- Host TISAX workshops for supplier teams
- Provide standard templates for questionnaire responses
- Establish a feedback loop for continuous improvement
Manufacturing Case Using Predictive Analytics
Sensors on CNC machines streamed data into AI models that flagged anomalies before failures. Monitoring 15 key metrics enabled 99.2 % equipment uptime and cut maintenance costs by 22 %.
Manufacturing Implementation Tips
- Conduct walkthroughs of dashboard alerts
- Adjust anomaly thresholds for seasonal variations
Learn more about these industry cases in our knowledge hub
Finance Case With Model Governance
A leading bank re-engineered its model governance to align with GDPR and audit standards. A three-tier approval process and automated alerts reduced manual oversight by 40 %, shortening audit preparation from weeks to days.
“Transparent governance turned audit preparation from weeks into days.”
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What Distinguishes Risk Management From Compliance In Enterprise AI?
Risk management identifies vulnerabilities and implements safeguards across the AI lifecycle. Compliance ensures adherence to legal requirements, industry standards and internal policies. Together, they minimize surprises and enhance resilience.
Q2: How Do I Choose The Right Frameworks For My AI Initiatives?
Map each AI use case to a framework’s core purpose:
- ISO 31000 for enterprise-wide risk management
- TISAX for sensitive automotive data
- GDPR for individual privacy rights
Consolidate controls to prevent overlap and assign clear responsibilities for each clause.
Q3: Which Roles Are Critical For Effective AI Governance?
At minimum:
- Chief Risk Officer
- Data Protection Officer
- AI Ethics Committee
Well-defined roles eliminate gaps and ensure accountability.
Q4: What Metrics Provide Board-Level Assurance?
Focus on:
- Number of Risk Incidents
- Mean Time to Resolve Issues
- Audit Finding Trends
- Training Completion Rates
Present these in an executive dashboard for clear, strategic discussions.
Presenting clear KPIs is essential for board-level visibility and confidence.
Looking for AI Expertise?
Get in touch to explore how AI can transform your business.
Key Governance Takeaway
Start risk management and compliance from day one. This proactive approach reduces surprises and builds stakeholder trust.
- Revisit these FAQs to stay aligned with evolving standards
- Engage key stakeholders early in the process
Ready to strengthen your risk management and compliance framework? Partner with Reruption GmbH for expert guidance and results-oriented AI governance.